In the tropics, milking dairy cows require 60 to 70 L of water per day for maintenance, plus an additional 4 to 5 L for each litre of milk produced. Water requirements increase as air temperature rises. A 4°C increase raises water consumption by 6 to 7 L/d. During the warmer season, high-yielding milking cows can consume 150 to 200 L of water per day. Dry matter intake, meal composition, humidity, wind speed, water quality (sodium and sulphate levels), and the temperature and pH of the drinking water are all elements that influence water consumption.
Energy is used for maintaining the cow’s normal metabolism. This includes breathing and maintaining body temperature. Physical activities such as walking and eating add to the maintenance requirement, as does environmental temperature and physiological state (ie pregnancy, lactation). With most cows in the tropics housed indoors, physical activity is negligible.
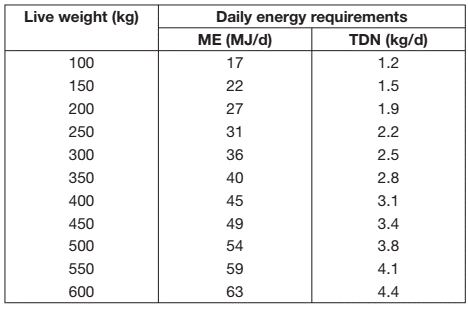
An small allowance for grazing and eating activity has been factored into the maintenance requirements. In flat terrain, an additional 1 MJ ME (or 0.1 kg TDN)/km should be added to provide the energy needed to walk to and from the dairy. In hilly country, this increases up to 5 MJ ME (or 0.4 kg TDN)/km walked throughout the day.
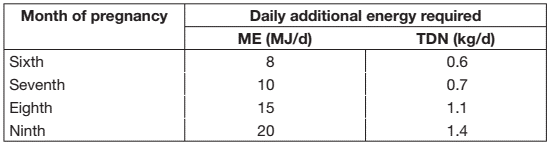
A pregnant cow needs extra energy for the maintenance and development of the calf inside her. From conception through the first five months of pregnancy, the additional energy required is about 1 MJ/d for each month of pregnancy. Energy requirements for pregnancy become significant only in the last four months.
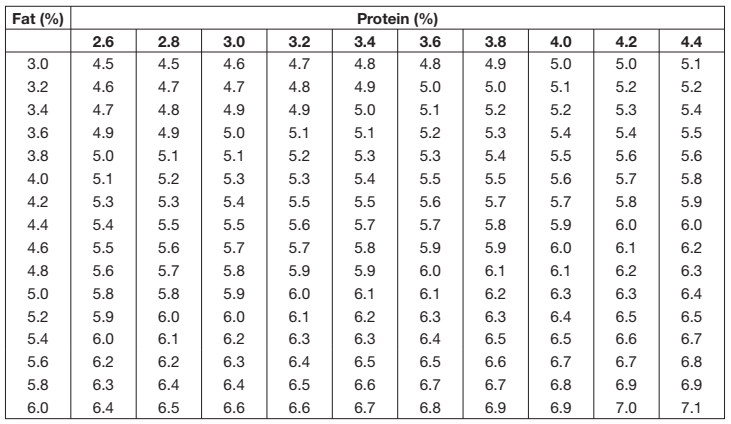
Energy is the most important nutrient to produce milk. The energy needed depends on the composition of the milk (i.e. fat and protein content). The following table present the energy needed to produce 1 L of milk with a range of fat and protein tests, in both MJ of Metabolisable Energy and kg of Total Digestible Nutrients. High testing milk might need 7.1 MJ of ME (or 0.5 kg TDN)/L, whereas low-testing milk might need only 4.5 MJ of ME (or 0.3 kg TDN)/L of milk.
Dairy industry in India do not measure protein contents of milk delivered from small holder farmers, alternatively using Solids-Not-Fat (SNF) content to measure non-fat milk solids. Solids-not-fat comprises the protein, lactose and minerals in milk, with lactose and mineral contents being relatively stable. Assuming lactose is 4.7% and minerals 0.7%, milk protein can be calculated as follows:
Milk protein (%) = SNF% – 5.4
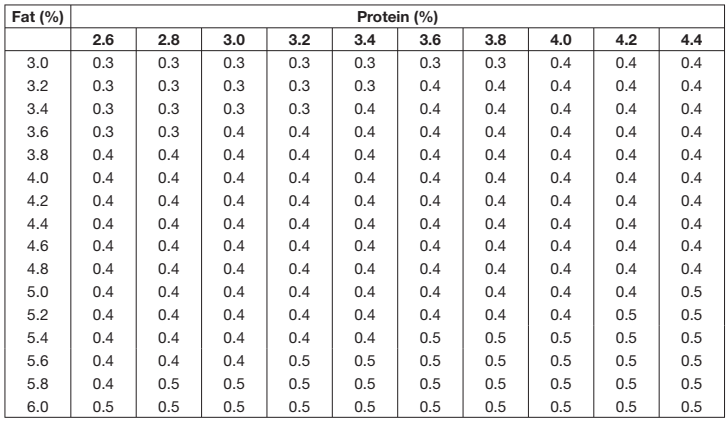
The following steps and the above tables can be used to calculate daily metabolizable energy requirements for:
• a 550 kg cow
• housed, hence with no activity allowance
• in the sixth month of pregnancy
• producing 13 L of milk (containing 3.6% fat and 3.2% protein),
Point one –> 59 MJ/d + 0 MJ/d + 8 MJ/d = 67 MJ/d (for maintenance, activity and pregnancy, respectively)plus
Point two –> 5.1 MJ/L milk for 13 L (= 5.1 MJ s 13 L) or 66 MJ/d for milk production, hence
Point three –> a total of 67 MJ/d + 66 MJ/d = 133 MJ/d.








